Imitation scams and how to stay safe

3 common ways scammers are trying to imitate ING
Scammers are becoming more sophisticated and some are even trying to impersonate ING. As flattering as it may be, they don’t have your best interests at heart like we do. So beware of imitations. Here’s how to identify 3 common types of scams and tips on how to avoid them.
1. Investment scams
Investment scams are schemes where scammers promise attractive returns on investments with the intention of stealing the hard-earned money you invest.
These scams often involve the presentation of fake investment opportunities and documents featuring the name of a trusted organisation – like ING – that seem too good to pass up.
But like most things in life, if it seems too good to be true it probably is.
Always check before you invest
Before you invest any money, it can pay to do your own research.
For a list of what to check, visit the check before you invest page at moneysmart.gov.au/check-and-report-scams/check-before-you-invest and the investor alert list at moneysmart.gov.au/check-and-report-scams/investor-alert-list
To protect yourself, you should be wary of offers that offer big returns for little risk.
Before handing over any money, always verify if an investment opportunity is genuine by consulting reputable sources and seeking professional advice.
Kai’s* investment story
ING customer ‘Kai’ received an email pretending to be from ING promoting a false fixed-term deposit investment. The email also included a link to a simulated ING-branded trading page and a fake ING-branded brochure and application form.
*Name changed for privacy.

2. Phishing scams
Phishing scams are where scammers attempt to trick you into revealing sensitive personal information like your bank account, password and credit card details. These scams often use fake emails or websites that mimic trustworthy brands like ING.
Knowing your phishing from your smishing
Phishing and smishing scams share similarities but employ different tactics.
While phishing scams primarily use fake emails and websites, smishing scams use SMS text messages to exploit the immediacy and familiarity of mobile devices and create a sense of urgency.
To avoid falling victim to phishing scams, never provide personal details or click links in unsolicited messages.
Trustworthy organisations will never ask you to reveal sensitive information by email or SMS. Always verify the authenticity of a communication by contacting the organisation directly using trusted contact details – not the contact details in the suspect communication.
Jared’s* phishing story
ING customer ‘Jared’ received an SMS about an unauthorised transaction in his account and to verify the addition of a new payee. The SMS contained a link which led to a fake ING webpage where Jared was asked to enter his ING client number and online banking access code.
*Name changed for privacy.
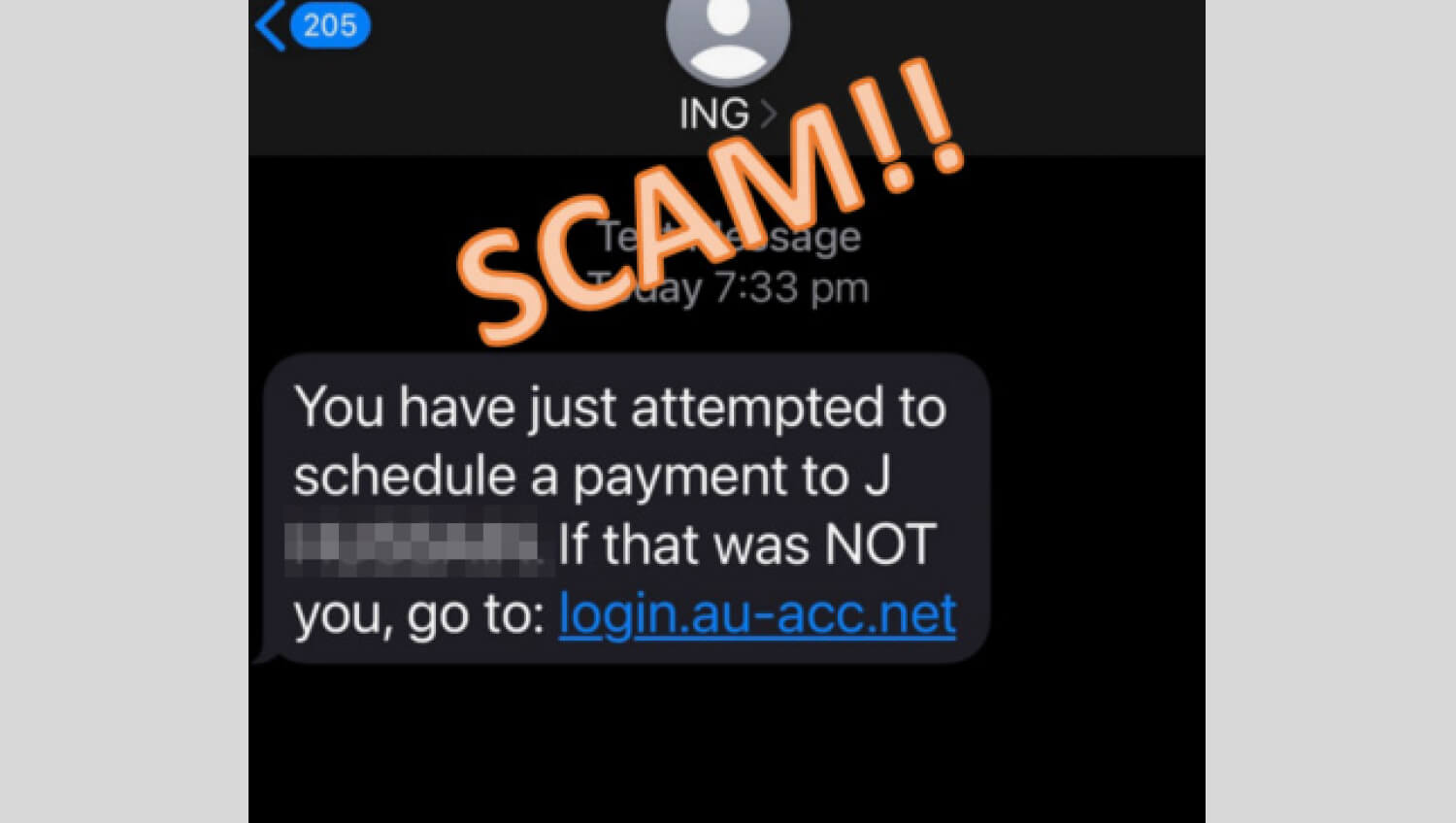
3. Impersonation scams
Impersonation scams are when scammers pose as a trusted organisation to trick you into handing over your money or personal information.
Currently scammers can even use technology to make their calls and SMS look like they’re coming from an organisation’s real phone number.
To protect yourself, always verify the identity of individuals or organisations making unusual requests, especially if they involve financial transactions. Double-check contact details and independently confirm the legitimacy of the request through reliable channels.
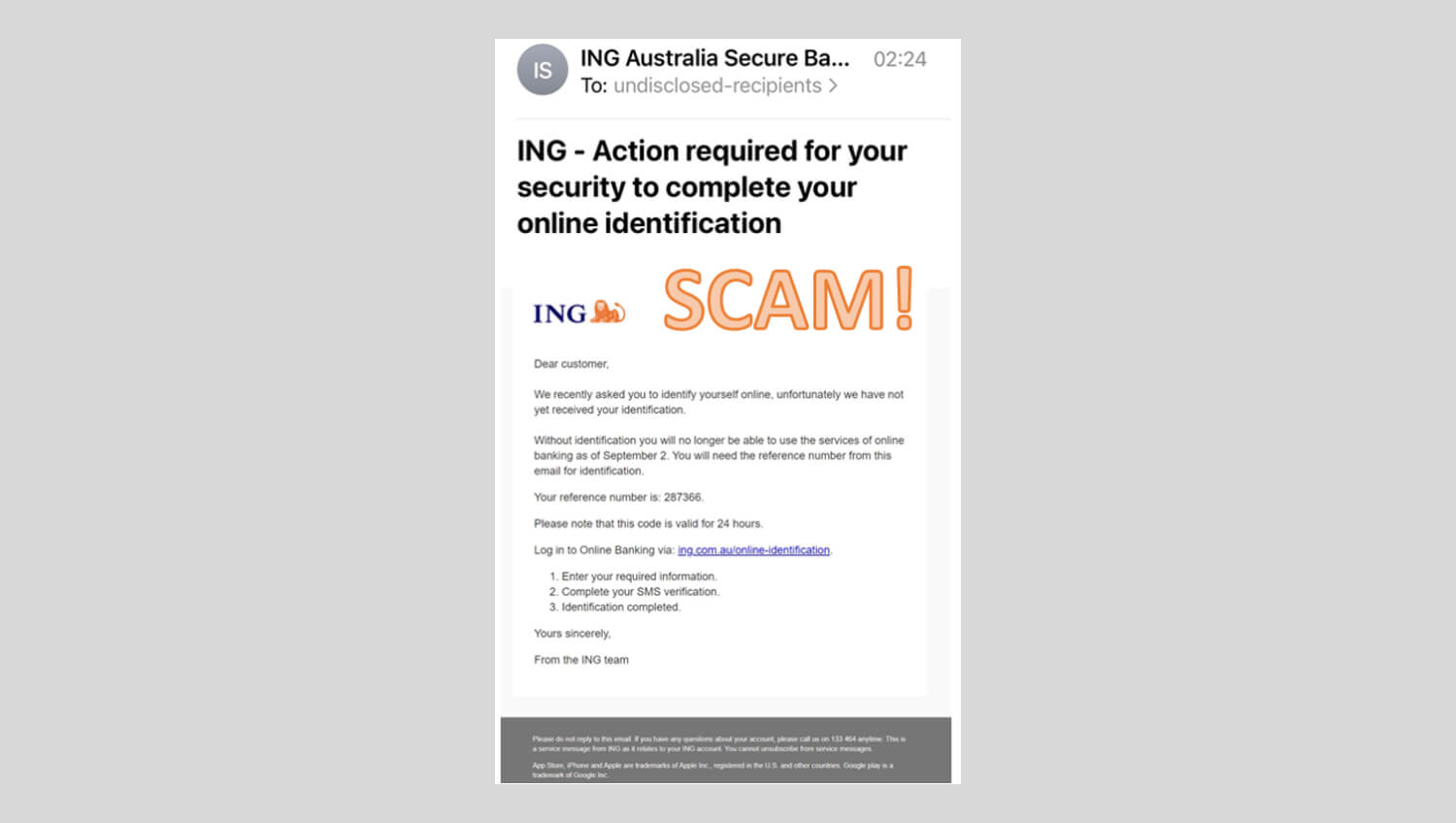
Sam’s* impersonator story
ING customer ‘Sam’ received an email pretending to be ING and asking them to verify their identification by clicking a link, to avoid online banking being suspended. The email contained a false link that simulated an ING online banking page.
*Name changed for privacy.
3 steps to help protect yourself
- Stop. Does something feel off or too good to be true? If so, it probably is.
- Reflect. Ask a trusted adviser or look up the official organisation and confirm with them.
- Protect. Hang up, don’t click anything or provide any details. If you’re an ING customer and notice unusual activity on your account, place your card on hold in the ING app and call our 24/7 scams line on 1800 052 74.
Staying up to date with the latest scams
By staying up to date with the latest scams and being cautious about online interactions, you can help reduce your risk of falling victim to a scam. To check for the latest scams targeting ING customers, bookmark our security alerts page at ing.com.au/security/latest-alerts.html
ING is not affiliated with third parties mentioned in this article. ING is not responsible for any services provided by third parties nor does ING accept any liability or responsibility arising in any way from any products or services supplied by the third parties.
The information is current as at publication. Any advice on this website does not take into account your objectives, financial situation or needs and you should consider whether it is appropriate for you. Deposit products, savings products, credit card and home loan products are issued by ING, a business name of ING Bank (Australia) Limited ABN 24 000 893 292, AFSL and Australian Credit Licence 229823. Living Super, a sub-plan of OneSuper ABN 43 905 581 638 is issued by Diversa Trustees Limited ABN 49 006 421 638, AFSL 235153 RSE L0000635. The insurance cover offered by Living Super is provided by Metlife Insurance Limited ABN 75 004 274 882, AFSL 238096. ING Insurance is issued by Auto & General Insurance Company Limited (AGIC) ABN 42 111 586 353 AFSL Licence No 285571 as insurer. It is distributed by Auto & General Services Pty Ltd (AGS) ABN 61 003 617 909 AFSL 241411 and by ING as an Authorised Representative AR 1247634 of AGS. All applications for credit are subject to ING’s credit approval criteria, and fees and charges apply. You should consider the relevant Product Disclosure Statement, Terms and Conditions, Fees and Limits Schedule, Financial Services Guide, Key Facts Sheet and Credit Guide available at ing.com.au when deciding whether to acquire, or to continue to hold, a product. Before interacting with us via our social media platforms, please take a minute to familiarise yourself with our Social Media User Terms https://www.ing.com.au/pdf/Social_Media_User_Terms.pdf.






